What Is Chaga Mushroom?
Chaga has been consumed for centuries in the East, most typically as tea, where its health benefits have been recognized for centuries and more recently scientifically validated. It is found growing on the north side of birch trees in forests of northern latitudes. Its technical name is Inonotus Obliquus. Dried, it is hard like wood. The outside has a charcoal appearance and the inside has a rich dark golden-brown hue.
How is it used?
I have really grown fond of drinking chaga tea. I buy the chunks that are about one inch by one inch. I make a batch using about a dozen of the chunks in a slow cooker and three quarts of water. I re-use the chunks three times, with 16 ounces less water each time. I like it plain, but sometimes will use a little honey or stevia as a sweetener. I will even add some to my post-workout protein recovery shake.
Active Compounds in the Chaga Mushroom
- Beta-D-Glucans which help balance the response of the body’s immune system. This means that chaga helps boosts the immune system when necessary, but slows it down when it’s overactive. This makes chaga a natural Biological Response Modifier (BRM).
- Betulinic acid found in chaga is able to break down LDL cholesterol–bad cholesterol–in the bloodstream.
- Polysaccharides within its chitin walls, which provide energy, cardiovascular health, intestinal and liver health, mood and promote healthy blood sugar levels.
- Phytosterols present in chaga, 45% is Lanosterol, 25% is Inotodiols and the remaining 30% consists of Ergosterol, Fecosterol, and several others. In vivo and in vitro testing shows a direct effect of both Lanosterol and Inotodiols on cancer cells, with lanosterol imparting a positive effect on viral compounds.
- Betulin and betulinic acid are powerful therapeutic agents that are currently being researched for their effects on supporting healthy cholesterol levels. In addition to their favorable benefits for maintaining a healthy cholesterol profile, cancer prevention and viral conditions.
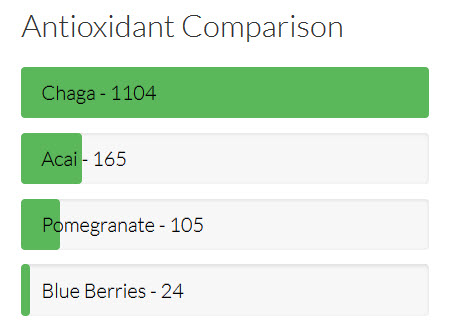
- Melanin, which has high antioxidant levels due to the amount of polyphenols it contains. In fact, chaga has the highest ORAC score (the measure of antioxidant potency) of any superfood.
- SODs are another important antioxidant present in chaga. SOD refers to a group of enzymes called Super Oxide Dismutase. These enzymes play an important role in protecting our body against the destructive effects of uncontrolled oxidation and free radicals. SOD potency is measured by the S-ORAC score.
Diseases and Conditions benefited by Chaga
- Immune Support- Viral Conditions & Cancer
- Free Radical Scavenging-
- Cardiovascular Disease-
- Intestinal Health
- Liver Health
- Blood Sugar
- Mood